Fountech Providing all types of quality RFID Door Lock System as well as Installation and Maintenance. The world is constantly moving towards modernization. In its continuation we are encouraging the use of state-of-the-art RFID door lock system for every hotel, resort, conference hall, office and any type of door lock system.
What is RFID Door Lock?
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a leading technology for a wide range of applications, from inventory tracking to payment processing. In terms of security, RFID door lock systems are very common for access control because they provide a reliable, consistent experience with trackable data. Like other traditional access control forms such as swipe cards, RFID locking systems are non-communicative, meaning the reader does not have to touch the certificate to perform the task.
Similar to a barcode reader, RFID readers work by sending and receiving data, but instead of scanning any code, the data is transmitted over radio frequencies. An RFID door locking system requires an RFID tag, an antenna, an RFID reader and a transceiver to function as a complete system.
In an RFID door lock access control system, the user’s credentials (usually a keycard or fob with an RFID chip) contain unique identifying information called a tag. When the user approaches the reader, the reader’s signal detects the information stored in the user’s RFID tag and sends the tag to the access control system via the access and transceiver for approval. Once read, the system will either accept or reject the request to unlock the door. Data is automatically saved from an RFID-enabled system so that access to the control system can be tracked.
Types of RFID Door Lock Systems
Due to the wide use, different types of RFID technology are available in the market. The biggest difference between RFID access control door locks is the frequency at which the system operates. There are three main types of RFID frequencies:
Low Frequency (LF) – Low frequency RFID readers operate at 125 kHz and have a reading length of about 10 cm which means the tag must be very close to the reader for communication. Due to the very close requirements for low frequency RFIDs, interference from other systems and channels is less likely. This is why low frequencies are common in RFID door access control applications. You will find low frequency RFID door locks for business entrances and commercial office doors where users are very close before unlocking the door. However, this may not be the best option in case there is more distance between the certificate tag, the reader and the entry.
High Frequency (HF) – This is the most common type of industrial commercial RFID door lock system. High frequency RFID readers operate at 13.56 MHz and have a reading range of up to 1 cm to 10 cm, so they are very versatile. One advantage of using high frequency RFID door locks for business entries is that they can be configured based on the layout of the reader’s space. Near Field Communication (NFC) operates at the same frequency as high frequency RFID, so you will often see high frequency RFID door locks that support NFC-enabled devices, mostly for payment processing and access control.
Ultra High Frequency (UHF) – This type of RFID access control technology typically operates at 900 MHz and has the longest reading range of up to 100 meters depending on the tag at the fastest reading speed. However, there is a risk of ultra-high frequency interference due to the long reading range. If not actively managed, interference can make UHF communication less reliable and create potential security risks if someone is trying to intercept data from RFID devices. That being said, UHF readers are typically used in parking garages and vehicle identification. With parking garage gates controlled by a commercial RFID door lock system, authorized vehicles can conveniently unlock the gate without taking their phone or scanning a badge at the gate.
There are three different types of RFID tags that work in different ways. An active tag transmits a constant signal and requires an uninterruptible power supply such as a battery. Active tags also have a built-in antenna to enable it to transmit and receive radio signals from other tags and nearby readers. Active tags support data read and write functions, so they are popular for logging or documentation purposes.
Semi-active tags for integrated circuitry also require battery power. Also known as battery-assisted passive tags (BAPs), these tags do not transmit their own signals until they reach the limits of an RFID access control door lock. Once they receive a signal from a nearby reader, the internal battery enables the communication needed to unlock the door.
The third type of RFID tag is called a passive tag. Passive RFID tags have no internal power source, instead an RFID door lock uses a magnetic field emission to induce a current in the tag’s built-in antenna. Passive tags are usually less expensive than active or BAP RFID tags.
Advantages of RFID Door Lock
- Cost-effective access control solution for internal doors
- One credential for every door in the building
- Combined dashboard for improved security monitoring
- Easy-to-deploy cloud integration with no additional wiring
- Complete access control for every door, across any size organization
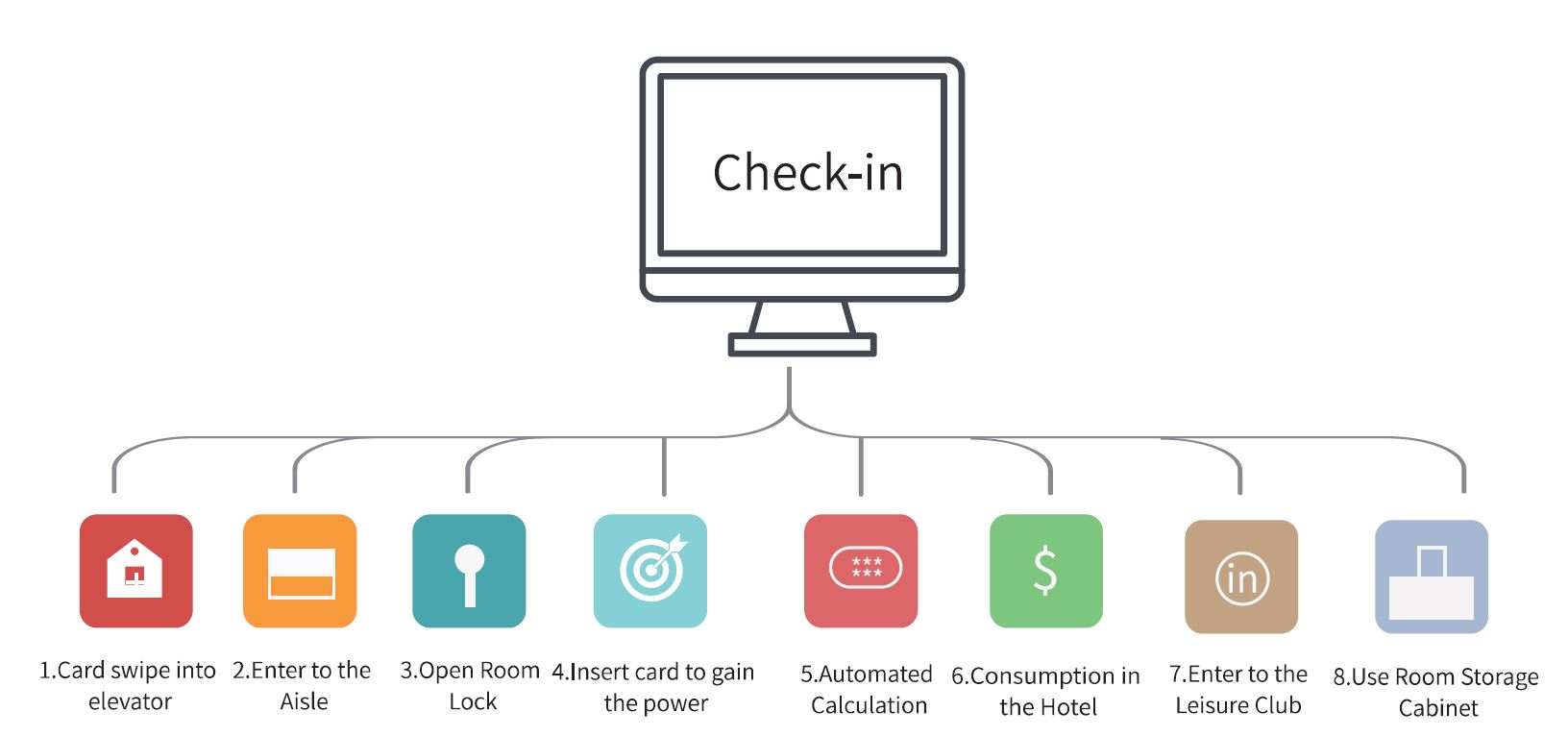
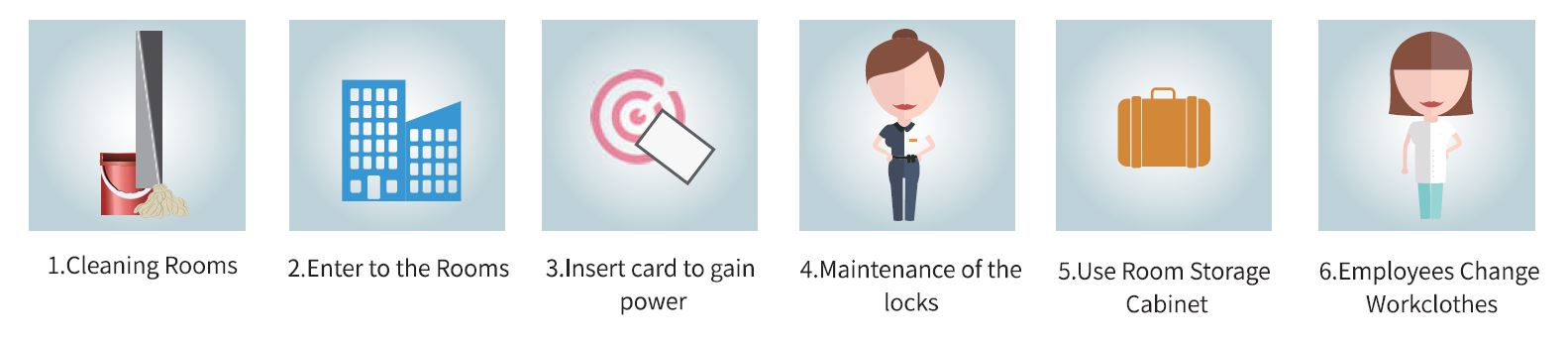
RFID Door Lock for Management System
Intelligent Hotel RFID Door Lock System is a software and hardware integrated system, which is composed of the following parts:
> Software system:
Operating system that can run Windows 3.1 or more.
> Management software:
The system is managed, including setting the function of door lock, restricting the authority of the cardholder, reading the record of unlocking, adjusting the clock in the lock, etc.
> Card making module:
Connect with computer USB interface, read and write the smart card.
> Smart cards are divided into:
Open card and management card.
> Open-door card is divided into five levels of management:
Room card, cleaning card, floor card, building card, general card.
> The functional distinction of management card includes:
Setting card, time card, record card, restriction card.
> IC card type:
TemicE5557/M1FARE-I card/apartment ID board.